
The Growing Demand for Efficiency
The Role of Industrial Conveyor Systems
- Precise movement of parts to the right location at the right time.
- Real-time data tracking for quality control and throughput analytics.
- Scalable flexibility, allowing reconfiguration as needs shift or production lines expand.
Dorner has played a pivotal role in advancing these systems, innovating designs that address a variety of conveyor capacity & load requirements while remaining easy to maintain and integrate.
Types of Industrial Conveyor Systems and Their Functions
1. Belt Conveyors
Belt conveyors feature continuous loops made of fabric or modular belts that move products from one point to another:
- Common Use Cases: Packaging, assembly lines, inspection stations.
- Advantages: Smooth material flow, adaptability for inclines/declines, efficient conveyor integration.
- Key Consideration: Proper tracking and tensioning to maintain performance.
2. Roller Conveyors
- Ideal For: Cartons, pallets, or other flat-bottomed products.
- Benefits: Low maintenance, ease of installation, scalable configurations.
- Drawback: Not as suitable for smaller or irregularly shaped items without additional guiding.
3. Flexible Chain Systems
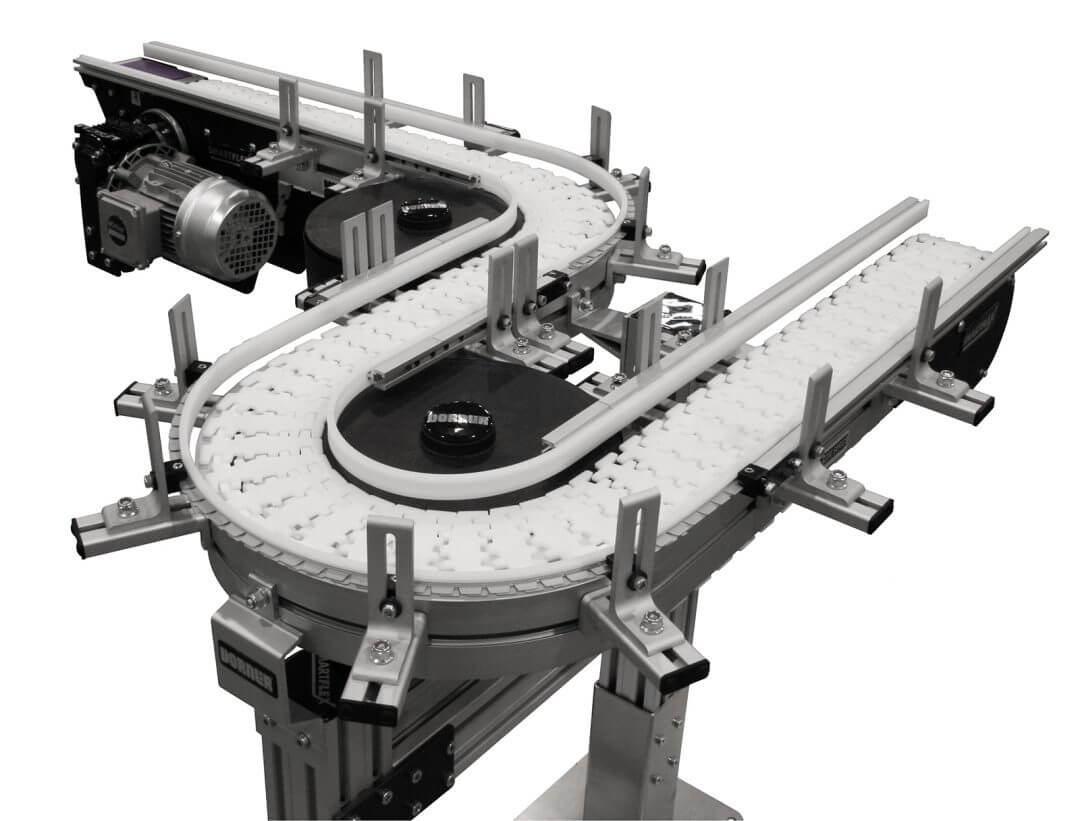
Flexible chain conveyors are similar to modular belt conveyors but unlike the mesh-style linking of modular belt components, flexible chain conveyors use a unique single-point link maximizing 3-dimensional flexibility. This unique feature makes these conveyors ideal for complex configurations with multiple curves and elevation changes on a single line. Flexible chain conveyors, like Dorner’s FlexMove, navigate tight spaces with curves and inclines:
- Where They Shine: Large or oddly shaped products, space-constrained layouts.
- Distinct Advantages: Adaptable routing, sturdy construction for heavy-duty conveyors.
- Key Note: Careful selection of chain material to match load and environmental conditions.
4. Overhead Conveyors
- Primary Industries: Automotive assembly, painting/coating processes.
- Pros: Maximizes space utilization, streamlined workflow.
- Cons: May require specialized maintenance and safety measures.
5. Specialized & Custom Conveyors
- Why Go Custom?: Unique product shapes, environmental regulations, or specialized throughput goals.
- Dorner’s Value: Expertise in designing conveyors to meet specific conveyor capacity & load requirements—from extra-wide belts to ultra-sanitary, stainless steel frames.
Major Industries Adopting Industrial Conveyor Systems
1. Automotive
- Reliability: Automated/robotic assembly, sensitive battery assemblies for EVs, and more.
- Advantages: Precise scheduling in assembly lines, reduced manual handling.
- Key Focus: Durability and production line optimization.
Dorner has played a pivotal role in advancing these systems, innovating designs that address a variety of conveyor capacity & load requirements while remaining easy to maintain and integrate.
2. Electronics
- Typical Products: Printed circuit boards (PCBs), microprocessors.
- Conveyor Must-Haves: ESD protection, minimal vibration, accurate positioning.
- Benefit: High reliability for delicate components.
In automotive or electronics facilities where floor space is at a premium, overhead monorail systems from montratec can efficiently transport parts and assemblies without congesting ground-level pathways.
3. Packaging
- Critical Needs: Rapid throughput, minimal downtime, easy changeovers for different package sizes.
- ROI Factor: Efficient conveyor integration with automated pack-off stations.
For high-volume packaging and bottling lines, specialized accumulation solutions from Garvey reduce downtime by buffering products whenever a downstream station experiences delays. This ensures continuous flow, even in complex production setups.
E-commerce & Distribution
- Focus: High-speed sorting, real-time tracking, and minimal error rates—achieved through the use of photo/vision sensors, RFID readers, and robust control systems.
- Key Benefit: Accurate handling of diverse product shapes and sizes, with integrated monitoring ensuring products are routed to the correct destination.
6. Medical & Pharmaceutical
- Requirements: Smooth transitions, minimal particle generation, precise indexing.
- Compliance: Regulatory standards for cleanliness and traceability.
Optimizing Production Flow with Conveyor Technology
Bottleneck Elimination
- Streamline Workflow: Automated conveyors continuously move materials and products from one station to the next, reducing idle time between steps.
- Improve Consistency: A stable, repeatable flow means fewer surprises and less downtime. Products don’t sit waiting for the next workstation, which keeps production moving smoothly.
- Balance Workload: When each station receives a consistent supply of parts, teams or automated machines can focus on their tasks without interruptions. This steady cadence allows managers to quickly identify and address any emerging slow spots.
Automation & Robotics Integration
- Enhanced Precision: Coordinating conveyor movement with robotic arms ensures each product reaches the robot’s workspace in a predictable manner, enabling precise picking, placing, or assembly.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Advanced conveyors can receive signals from sensors or a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) to speed up or slow down based on changing throughput requirements, ensuring you meet production targets with minimal downtime.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automating tedious or repetitive tasks frees up operators to focus on higher-value responsibilities such as quality control or process improvement.
Safety & Ergonomics
- Lower Risk of Injuries: By reducing the need for heavy lifting, manual handling, or repetitive motions, conveyors help prevent common workplace injuries like muscle strains and back pain.
- Built-In Safety Measures: Guardrails, emergency stops, and sensor-based safety systems can detect jams or blockages and automatically halt the conveyor to prevent accidents.
- Improved Work Environment: A well-designed conveyor layout keeps aisles clear and reduces clutter. This added organization improves visibility and helps workers navigate the production floor more safely.
Scalability & Adaptability
Manufacturing demands can shift rapidly, whether due to changes in market conditions, product lines, or seasonal peaks. Industrial conveyor systems that prioritize modularity and adaptability give you the flexibility to adjust on the fly:
- Modular Components: Many of today’s conveyors use standardized modules, making it easy to add extensions, change the layout, or even move entire conveyor sections to different parts of your facility.
- Future-Proof Investment: As industrial automation trends evolve, having conveyors that can accommodate new technologies (such as AI-based inspection tools or additional robotic arms) ensures your investment remains viable for years to come.
- Customized Configurations: Whether you need inclines, declines, curves, or a combination of all three, configurable conveyors can be tailored to unique production spaces, ensuring products travel the most efficient route possible.
In addition to ground-level conveyor lines, monorail solutions from montratec can help optimize production flow by utilizing vertical space. Meanwhile, Garvey’s accumulation systems can be integrated to prevent product backups and ensure seamless throughput—particularly vital in fast-paced packaging and bottling operations.
Dorner’s Innovative Approaches
Custom-Engineered Solutions
- Low-Profile Designs: Fit under press machines or in tight production lines.
- Sanitary Designs: Speed up cleaning processes and meet FDA guidelines.
Industry-Leading Lead Times & Warranty
- Fast Shipping: Many conveyors ship in as few as 3-5 business days.
- Extended Warranty: Dorner’s 10-year coverage reflects their product confidence.
Smart Conveyor Systems
- Sensors & IoT: Real-time data collection, predictive maintenance alerts.
- Compatibility: Integrates seamlessly with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems).
Global Support Network
With facilities in the U.S., Germany, Mexico, and Malaysia, Dorner delivers:
- Localized Expertise: Quick installation and after-sales service.
- Streamlined Parts Availability: Reduced downtime and maintenance costs.
Reducing Downtime & Boosting Throughput
Preventive Maintenance Programs
- Focus Areas: Belt tension, motor bearings, sensor calibration.
- Benefit: Minimizes unexpected halts in production.
High-Speed Applications & Precision
- Industry Challenge: Meeting high output demands without compromising on quality.
- Dorner’s Solution: Heavy-duty conveyors engineered for speed and durability.
Real-Time Monitoring & Troubleshooting
- Instant Alerts: Flag misalignments or motor inefficiencies early.
- Proactive Resolutions: Maintenance teams can address issues before major disruptions occur.

Future Trends in Industrial Conveyors
Industrial conveyors have continually evolved to meet the growing demands of modern manufacturing. As industrial automation trends push the boundaries of speed, efficiency, and data-driven operations, conveyor technology is evolving in exciting new ways. Below are the key trends set to define the next wave of conveyor innovation.
Industry 4.0 & IoT Integration
- Real-Time Monitoring: Conveyor systems equipped with sensors, smart controllers, and IoT devices can track operational metrics—such as motor temperatures, belt speeds, and throughput—in real time. This enables instant adjustments and swift resolution of any emerging issues.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing sensor data, manufacturers can identify when components are nearing failure. Instead of reacting to sudden breakdowns, teams can plan maintenance schedules that minimize downtime, increasing production line optimization.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Seamless communication between conveyors, robotic stations, and a central Manufacturing Execution System (MES) boosts overall operational efficiency. Managers can monitor all parts of the process from a single dashboard, ensuring that production goals are consistently met.
Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Materials
- Energy Efficiency: As sustainability becomes a cornerstone of manufacturing, conveyor systems are increasingly designed with high-efficiency motors, optimized gearboxes, and advanced controls that reduce power consumption.
- Low-Impact Materials: From eco-friendly belt compounds to recyclable structural components, conveyor designers are exploring ways to reduce their environmental footprint. This approach aligns with broader corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals and consumer expectations for greener products.
- Long-Term Durability: A sustainable system is not just about initial materials—it’s also about longevity. High-grade components that last longer reduce waste, curb maintenance costs, and support a more sustainable supply chain.
Advanced Robotics & AI
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Next-generation factories increasingly feature cobots that work side by side with human operators. Conveyors designed to seamlessly interface with cobots can significantly speed up workflows by delivering parts and materials right where they’re needed.
- AI-Driven Vision Systems: Integrated vision technologies can identify, inspect, and sort items as they travel along the conveyor. For instance, AI-powered cameras can detect product defects or measure dimensions with extreme precision, ensuring top-notch quality control.
- Dynamic Routing: By combining AI algorithms with real-time data, some conveyor systems can dynamically re-route products. If a station is congested, the conveyor automatically shifts goods to a different line, preventing bottlenecks and further enhancing manufacturing automation.
Flexible & Modular Designs
- Reconfigurable Layouts: As production demands change—whether due to new product lines, seasonal spikes, or facility relocations—modular conveyors can be quickly adapted with minimal disruption. This flexibility is crucial for businesses that need to stay agile in fast-paced markets.
- Scalable Solutions: Instead of purchasing entirely new systems, manufacturers can simply add or remove conveyor modules to adjust capacity. This not only saves on capital expenditures but also allows for gradual growth without significant downtime.
- Plug-and-Play Integration: Conveyors are increasingly being built with standardized components that “plug-in” to larger automation ecosystems. Operators can mix and match components (like sensors, drives, or control panels) to create a system tailored to their exact needs.
Human-Centric Design & Ergonomics
- Operator-Friendly Interfaces: As automation becomes more complex, intuitive control panels and user-friendly software ensure operators can easily monitor and manage conveyor operations.
- Reduced Noise & Vibration: New belt materials and advanced drive systems aim to create a more comfortable work environment by minimizing vibration and decibel levels. This can lead to higher operator satisfaction and fewer workplace distractions.
- Safety Innovations: From improved guarding systems to advanced sensor arrays that halt conveyors when an obstruction is detected, conveyor technology is making worksites safer than ever.
As conveyor systems become more adaptable, eco-friendly, and data-centric, they will continue to play a pivotal role in heavy-duty conveyors and manufacturing automation for years to come.
Takeaways
Key Points to Remember:
- Modern conveyor systems offer scalability, adaptability, and the potential for real-time data insights.
- Industries ranging from automotive to food and beverage rely on conveyors for a competitive edge.
- Proactive maintenance and smart system monitoring are essential for minimizing downtime and maximizing ROI.
If you’re ready to explore how conveyors can supercharge your manufacturing operations, contact Dorner today.
By focusing on the transformative potential of industrial conveyor systems and leveraging Dorner’s expertise, you can stay on the cutting edge of manufacturing innovation.





